Services
NGS
Targeted Methylation Sequencing
Targeted Methylation Sequencing allows the detection of the methylation levels of the four nucleotides that can be methylated in genomic regions such as CpG islands and promoter regions.
It is possible to identify the methylation pattern of key regions using a smaller amount of sequencing data than whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. DNA methylation data plays a central role in studying biological phenomena such as gene expression, embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation, and chromosomal stability. Abnormal DNA methylation is also associated with DNA instability which can lead to human diseases such as cancer.
Application
- Profiling dysregulation of DNA methylation
- Studying genotype-environment interactions and disease-related patterns
- Investigation of individual variation in disease susceptibility
Sample/Laboratory Information
| Sample Requirement | gDNA > 3µg (minimum 2µg),60ng/µl, DIN > 6 |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | Agilent |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000 |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | ≥ 20 million read pairs per sample |
Bioinformatics
- Workflow
-
-
Standard Analysis
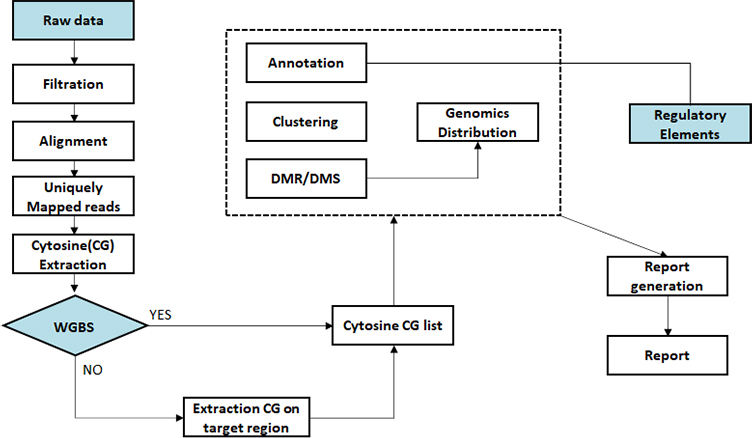
Sequencing data preprocessing
Alignment bisulfite sequencing data to genome
Methylation calling
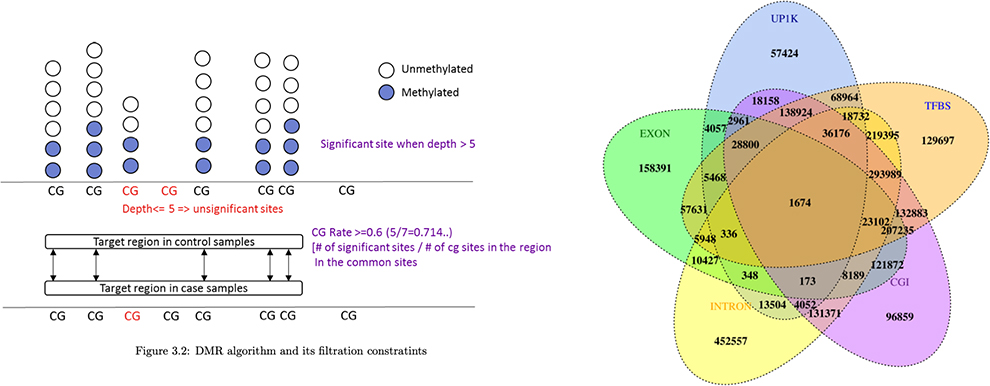
Differential methylated region (DMR) analysis
Differential methylated region (DMR) annotation
Reference
[1] Shin, H. Y. et al., (2020). Alteration in global DNA methylation status following preconditioning injury influences axon growth competence of the sensory neurons. Experimental neurology, 326, 113177.
[2] Kato, N. et al., (2015). Trans-ancestry genome-wide association study identifies 12 genetic loci influencing blood pressure and implicates a role for DNA methylation. Nature Genetics, 47(11), 1282–1293. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3405

Bisulfite Sequencing
Bisulfite sequencing is a method used to determine the DNA methylation level of cytosine contexts (CpG, CHG, CHH) on the entire genome. It is used to study epigenetic phenomena at the molecular level and can identify differentially methylated regions between samples or groups. The genomic contents of these regions can be annotated to understand their impact on gene expression. Theragen Bio has conducted research on Platycosides biosynthesis using whole genome bisulfite sequencing data obtained from Doraji (a type of Korea ginseng).
Application
- Profiling DNA methylation
- Studies on phenotypic diversity and evolution in plants and animals
- Understanding of epigenetic alternations of pathogenetic pathways
- Early diagnosis of diseases and cancers through the detection of DNA hypermethylation or hypomethylation
Sample/Laboratory Information
| Sample Requirement | gDNA > 3µg (minimum 2µg),60ng/µl, DIN > 6 |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | Swift |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000 |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | For effective sequencing depth 50X |
Bioinformatics
- Workflow
-
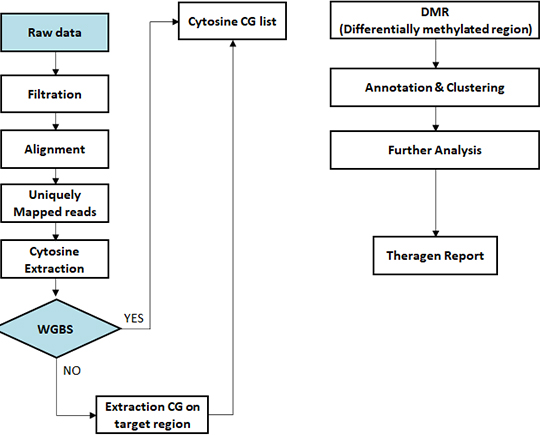
-
Standard Analysis
Reference building for non-human species
Sequencing data preprocessing
Alignment bisulfite sequencing data to genome
Methylation calling
All cytosine context (CpG, CHG, CHH)
Differential methylated region (DMR) analysis
Differential methylated region (DMR) annotation
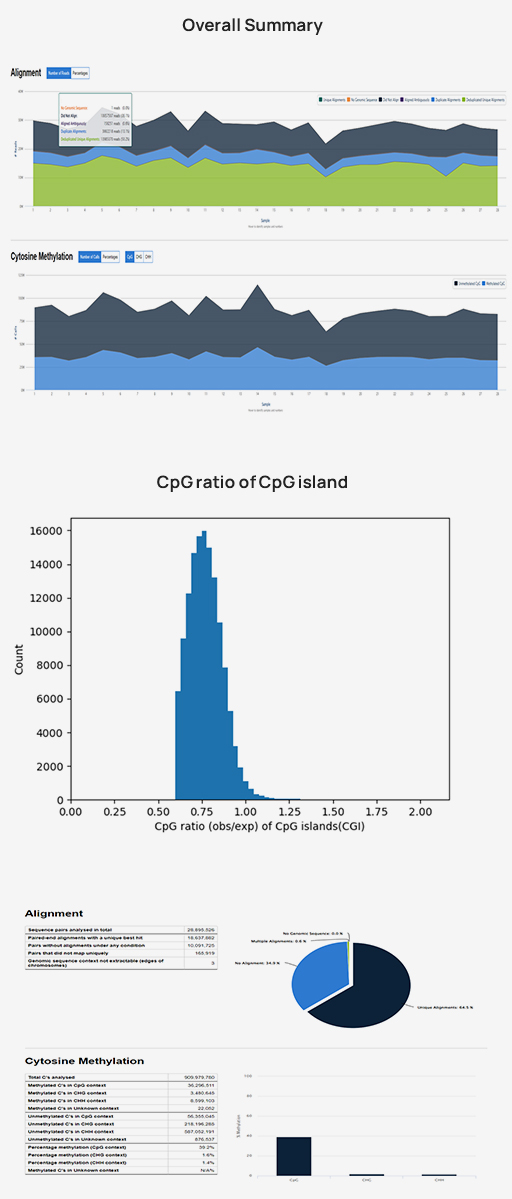
-
Advanced Analysis
Methylation rate (CpG, CHG, CHH)
Methylation pattern (Upstream, Genebody, Downstream)
Density of differentially methylated cytosines (DMCs)
No content
No content
No content
No content
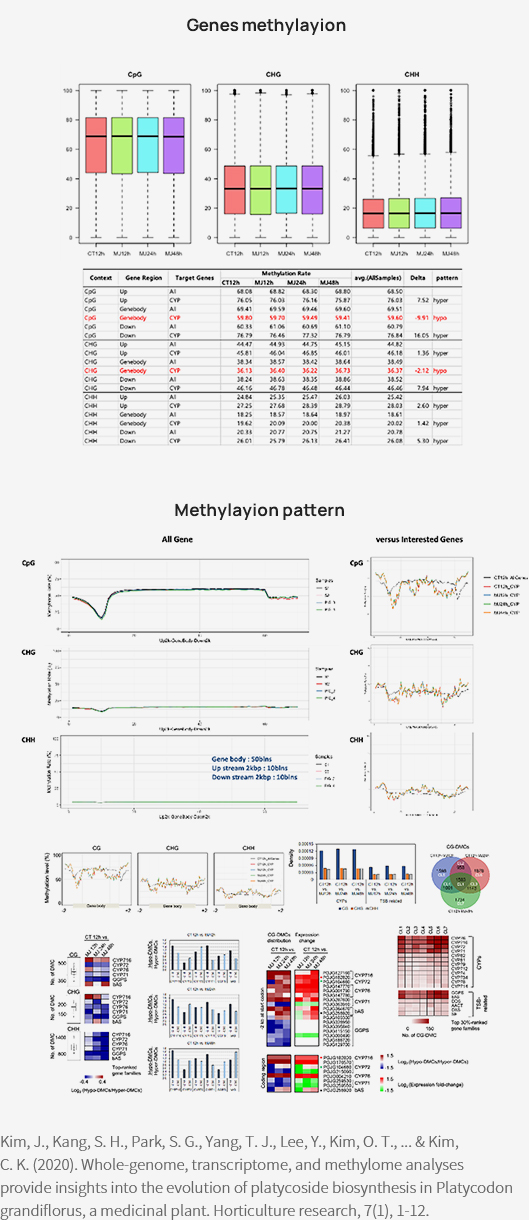
Reference
[1] Kim, J. et al., (2020). Whole-genome, transcriptome, and methylome analyses provide insights into the evolution of platycoside biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus, a medicinal plant. Horticulture research, 7, 112.

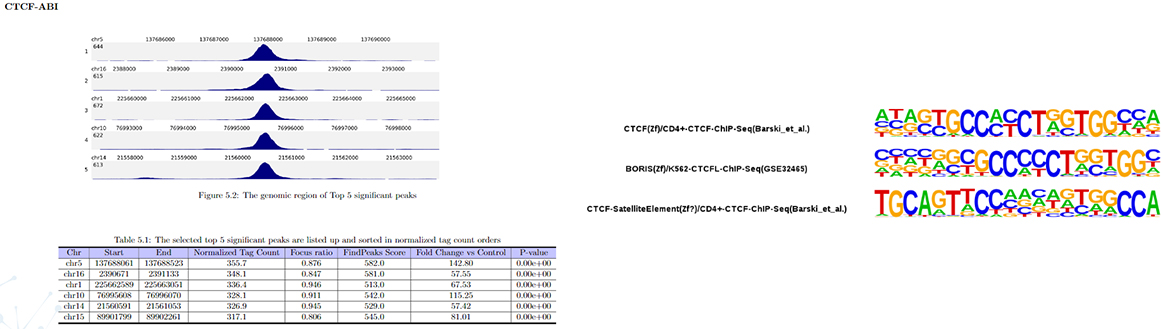
ChIP Sequencing
ChIP sequencing is a sequencing method that combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with NGS and allows for the identification of DNA-protein binding sites through bioinformatics analysis. The identified binding sites can accurately predict the epigenetic state of each cell type and are essential for understanding the regulation of cellular processes, cell differentiation, or disease progression mechanisms. Since ChIP sequencing uses immunoprecipitation methods, there may inevitably be technical biases, but these can be reduced through precise experimental design using background controls such as IgG and computational analysis methods.
Sample/Laboratory Information
| Sample Requirement | gDNA > 3µg (minimum 2µg) |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | Illumina |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000 |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | ≥ 20 million reads per sample |
Bioinformatics
- Workflow
-
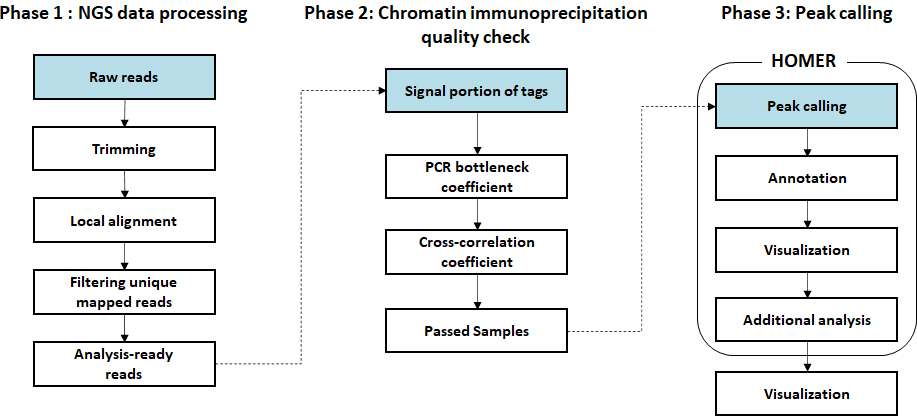
-
Standard Analysis
Sequencing data preprocessing
Local alignment to genome
Chromatin immunoprecipitation quality check
Peak calling
Peak annotation
Transcription factor motif analysis