Services
서비스
NGS
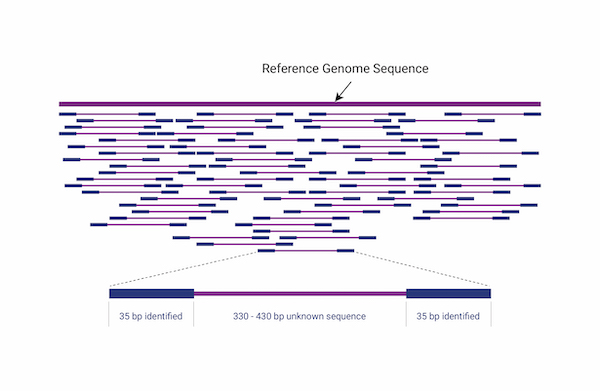
Whole Genome Resequencing
유전체 전체를 해독하는 전장유전체분석(Whole genome sequencing)은 전체 유전체를 해독하므로 유전체의 Germline,
Somatic 변이 및 CNV(Copy number variants), SV(Structure variants) 변이 등 유전체 전반의 변이 분석을 종합적인 측면에서 제공할 수 있습니다.
비 모델 종의 WGRS (whole Genome Resequencing) 분석은 컨설팅 후 Custumized 분석으로 비 모델 종의 Reference 크기 및 Annotation 정보 분석 등이 진행됩니다.
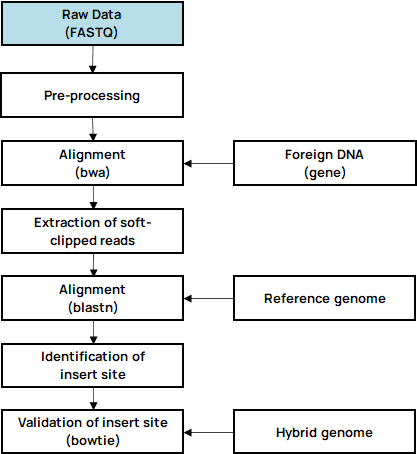
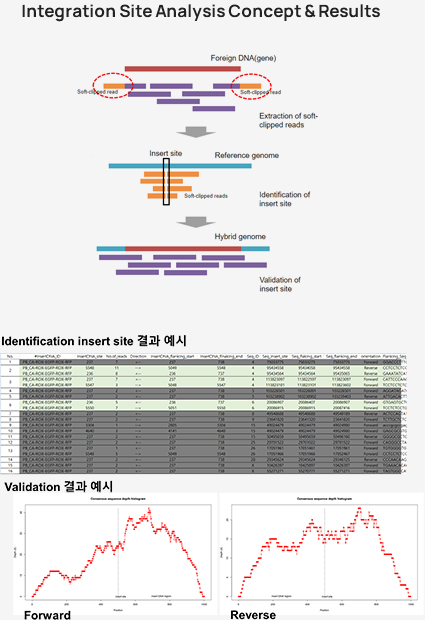
Customized 분석 중 Integration site analysis는 Host genome DNA에 삽입된 Vector (or Interagted gene) 의 위치를 Bioinformatics 기술 기반으로 식별하는 분석입니다.
Vector는 종류에 따라 다양한 방법으로 Host genome에 통합되기 때문에 Target gene 또는 Oncogene 등의 발현에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
따라서 삽입된 위치를 식별하는 것은 유전자 재조합 연구에 매우 중요합니다.
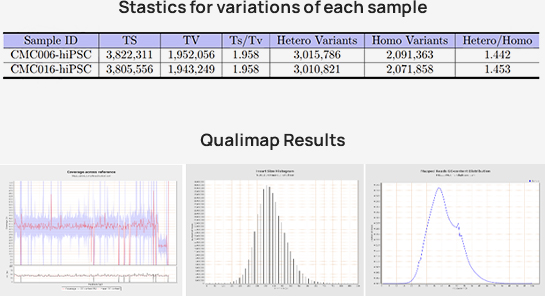
테라젠바이오는 차세대 염기서열 분석(NGS) 데이터를 매우 빠르게 분석하고 정확도를 높이기 위해 DRAGEN Bio-IT Platform을 도입했습니다. 매핑, 맞춤, 정렬, 중복 표시 및 하플로타입 이형 호출에 최적화된 알고리즘을 제공하는 생물 정보학 파이프라인을 통해 생식선, 체세포(종양 및 종양/정상), RNA, 단일 세포 RNA, 메틸화, 관절 유전형 분석 및 DRAGEN-GATK가 가능합니다. Germline 기준 WGS 샘플당 분석 시간은 40분~1시간 정도 소요되며 동시에 대량의 샘플을 분석해 낼 수 있으며,
Somatic 분석의 경우 샘플당 1시간 소요로 3일 동안 300개의 샘플을 분석할 수 있습니다. 테라젠바이오는 국내 최초로 Illumina ICA를 도입하여 성공적으로 운영하였으며,
AWS cloud 환경에서도 게놈 분석이 가능함에 따라 현재까지 5천 건 이상의 WGRS 샘플을 빠르게 분석하여 성공적으로 과업을 달성하고 있습니다.
적용 가능 연구
- Population genetics
- Genetic rare diseases
- Cancer research
샘플&실험정보
| Sample Requirement | gDNA > 500ng (minimum 100 ng), 5 ng/µl, DIN > 6 |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | Illumina, Pacbio |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000, Pacbio Sequel Ⅱ |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | For rare disease >30X |
생명정보학 분석
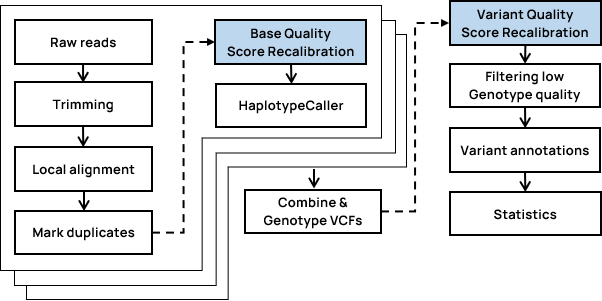
- WGRS Workflow
- Insertsite Workflow
-
Standard Analysis
Read mapping
Variants calling
Variant annotation
No content
-
Advanced Analysis
Somatic variants calling
Copy number variants(CNV)
Structure variants(SV)
Multisample variants calling
Integration site analysis
Features & Benefits
- 다양한 모델 종 및 비 모델 종에서의 WGRS 분석 경험 보유
- 한국인 칩 프로젝트와 같은 대용량 분석 경험 보유
Reference
[1] Ahn, S. M. et al., (2009). The first Korean genome sequence and analysis: full genome sequencing for a socio-ethnic group. Genome research, 19(9)
[2] Gallego Llorente, M. et al., (2015). Ancient Ethiopian genome reveals extensive Eurasian admixture throughout the African continent. Science (New York, N.Y.), 350(6262), 820–822.
[3] Kim, M. Y. et al., (2010). Whole-genome sequencing and intensive analysis of the undomesticated soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.) genome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(51), 22032–22037. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009526107
[4] Yoon, K. et al., (2013). Comprehensive genome- and transcriptome-wide analyses of mutations associated with microsatellite instability in Korean gastric cancers. Genome Research, 23(7), 1109–1117. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.145706.112
[5] Xu, X. et al., (2013). The Genetic Basis of White Tigers. Current Biology, 23(11), 1031–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.04.054
[6] Li, E. et al., (2020). Neural stem cells derived from the developing forebrain of YAC128 mice exhibit pathological features of Huntington’s disease. Cell Proliferation, 53(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12893
Whole Genome De novo Sequencing
PacBio 기반 Long-read sequencing 기술을 활용한 표준 신생 조합 유전체 분석(Whole-genome De novo sequencing)은
유전자원 확보를 위한 동물, 식물, 미생물 유전체가 주 분석 대상이 됩니다. 일반적으로는 식량자원부터 연구 결과물들이 보고가 되고 있으며,
최근에는 낮아진 염기서열 해독비용에 따라 유용 유전자원들에 대한 유전체 정보 확보를 위하여 표준 유전체 조립 분석을 진행하여,
각종 유전자원에 대한 특이적 기능을 가지고 있는 유전자들을 발굴하기 위한 기초가 되고 있습니다
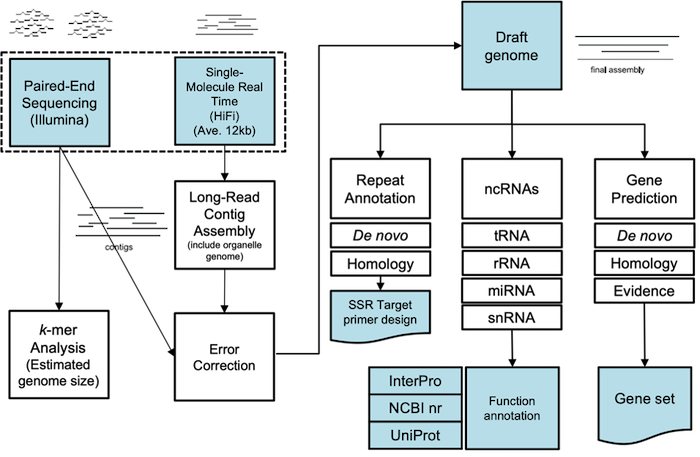
Repeat 모델을 이용한 Transposon 예측과 구조적 특성에 따른 분류하고, 유전체 서열 상의 Simple sequence repeat (SSR 또는 Microsatellite)를 추출하고 Primer를 제작합니다.
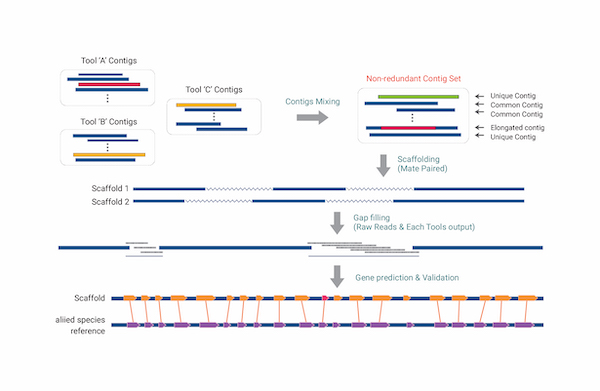
최종 Gene set에 대해 상동성 검색을 기반으로 유전자 기능 예측이 가능하며, Hybrid assembly는 서로 다른 시퀀싱 기술을 결합하여 조립하는 방법으로 완성도와 정확도 측면에서 뛰어납니다. 자사 보유 장비인 PacBio Sequel II의 Long high-fidelity (HiFi) reads는 99.9%의 정확도의 평균 13.5 kb 길이로 생산되며, Illumina short reads와 함께 조립하여 정확도 높은 Draft genome을 제공합니다. 조립된 Draft genome은 근연종을 참조하거나 RNA-seq 또는 Iso-Seq을 통해 유전자모델을 결정한 뒤 UniProt, NCBI nr, InterProScan, Pfam 데이터베이스와의 상동성검색으로 생물학적 기능 및 단백질 도메인 정보를 예측합니다.
적용 가능 연구
- Phylogenetic classification
- Species diversity studies
샘플&실험정보
| Sample Requirement | gDNA > 2µg (min 500 ng), 20 ng/µl, DIN > 6 |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | Illumina, PaBbio |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000, PacBio Sequel Ⅱ, PacBio Revio |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | ≥ 10 milion read pair per sample |
생명정보학 분석
- Workflow
-
Standard Analysis
Genome denovo assembly
Genome annotation
Error correction
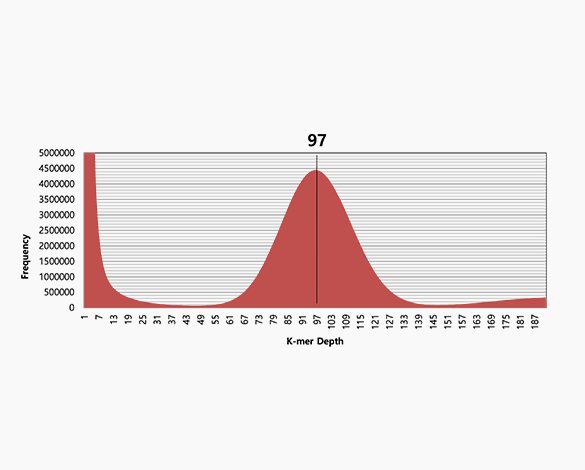
k-mer analysis
-
Advanced Analysis
Construction of mitochondrial genome
Construction of chloroplast genome
Phylogenetic analysis
No content
Reference
[1] Yim, H. S. et al., (2014). Minke whale genome and aquatic adaptation in cetaceans. Nature genetics, 46(1), 88–92.
[2] Cho, Y. S. et al., (2013). The tiger genome and comparative analysis with lion and snow leopard genomes. Nature communications, 4, 2433.
[3] Choo, J. H. et al., (2016). Whole-genome De novo sequencing, combined with RNA-Seq analysis, reveals unique genome and physiological features of the amylolytic yeast Saccharomycopsis fibuligera and its interspecies hybrid. Biotechnology for biofuels, 9, 246.
[4] Kim, J. et al., (2020). Whole-genome, transcriptome, and methylome analyses provide insights into the evolution of platycoside biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus, a medicinal plant. Horticulture research, 7, 112.
[5] Park, S. G. et al., (2021). Draft Genome Assembly and Transcriptome Dataset for European Turnip (Brassica rapa L. ssp. rapifera), ECD4 Carrying Clubroot Resistance. Frontiers in genetics, 12, 651298.
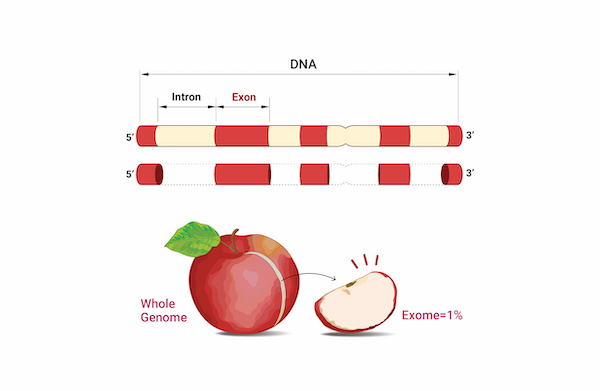
Whole Exome Sequencing
인간 유전체 정보가 보다 방대해지고 다양한 질병과 현상에 대한 유전체 정보가 구축되면서
전체 엑솜 분석(Whole exome sequencing)을 통해 더욱 많은 정보를 획득하는 것이 가능해졌습니다.
전체 유전체 중에서 단백질을 직접 코딩하는 Exome 영역 (휴먼의 경우 전체 유전체의 2% 미만)에 대해서 높은 Depth로 Germline 및 Somatic 변이체 정보를 제공하고 있습니다. Annotation된 Variant에 대한 카테고리별 및 기능별 분류하며, 임상적으로 유의한 변이 정보를 제공합니다.
적용 가능 연구
- Genetic disease-related studies
- Cancer research and drug development
- Pathogenic mechanism and molecular characterization
샘플&실험정보
| Sample Requirement | gDNA 500ng (minimum 50ng) 10 ng/µl, DIN > 6 |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | SureSelect(Agilent), Twist, etc |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000 |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | ≥100X (For tumor, ≥200X) |
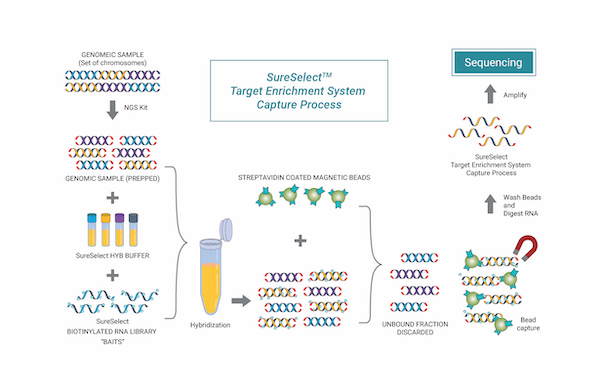
생명정보학 분석
- Workflow
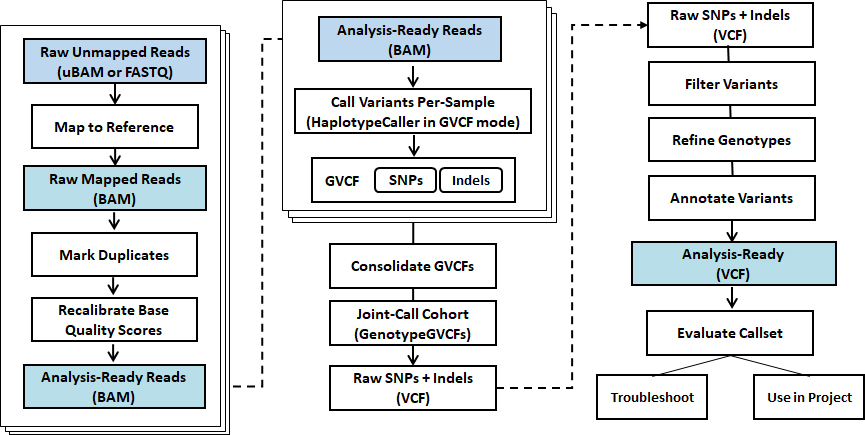
-
Standard Analysis
Germlin & Somatic
Read mapping + BQSR, VQSR
Variant calling (SNV, Indels)
Variant annotation
-
Advanced Analysis
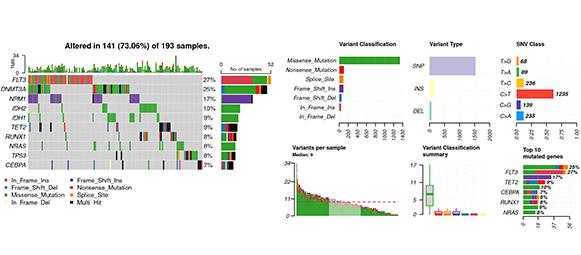
Oncoplot
No content
No content
No content
No content
Features & Benefits
- 다양한 분야에 적용가능한 변이체 탐색
- 단백질 영역에 대한 서열 정보에 있어서 높은 커버리지 확보 가능
- 전장 분석 기술 대비 더 빠르고 다루기 쉬운 데이터 생산
Considerations
- 생산된 데이터에 대한 확보할 커버리지의 양
- Hybrid capture kit에 따라서 다양성(Variability)이 존재 가능
- 커버리지 확보가 어려운 영역들 (Repeat elements, Tandem repeats and Psudogenes) 존재
- 극단적인 GC 비율이 존재하는 영역의 존재
Reference
[1] Phi, J. H. et al., (2018). Genomic analysis reveals secondary glioblastoma after radiotherapy in a subset of recurrent medulloblastomas. Acta neuropathologica, 135(6), 939–953.
[2] Chang, Y. H. et al., (2016). Use of whole-exome sequencing to determine the genetic basis of signs of skin youthfulness in Korean women. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 31(3), e138–e141. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.13904
Targeted Sequencing
Targeted sequencing은 초고해상도로 변이 분석을 할 수 있는 장점을 가지고 있어, FFPE(Fromalin fixed paraffin embedded)와 같이
정제도가 떨어지는 조직 샘플에서도 체세포 돌연변이를 검출할 수 있습니다. 암 등의 질환 관련 유전자 발굴 등 타겟으로 하는
유전자 및 보고자 하는 영역이 명확한 경우에 가장 적절하여 임상 검사실에서 가장 많이 사용하는 검사 방법입니다.
* 액체 생검(Liquid biopsy) : 소량의 혈액만으로 혈액 속에 떠다니는 암세포 DNA의 변이를 정확하게 분석하는 서비스로,
NGS기반으로 검출한계 0.01% 이하에서도 재현성 있게 암 체세포 변이(Cancer somatic muation)를 검출할 수 있습니다.
단일 혈액 튜브에서 분석을 실시하는 각 분석은 샘플에서 자주 변이되는 단일 뉴클레오티드 변이체와 짧은 Indel을 분석하는 데 사용됩니다.
적용 가능 연구
- Tumor mutation burden(TMB)
- Disease or phenotype-related studies
- Detection of low-frequency alleles and rare variants
- Identification of causative novel or inherited mutations
- Drug response and discovery of therapeutic targets
샘플&실험정보
| Sample Requirement | gDNA > 700ng (minimum 500 ng), 10 ng/µl, DIN > 6 |
|---|---|
| Library Kit | Agilent, Twist |
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq6000 |
| Recommended Sequencing Depth | 200X, 500X, 1000X |
생명정보학 분석
- Workflow
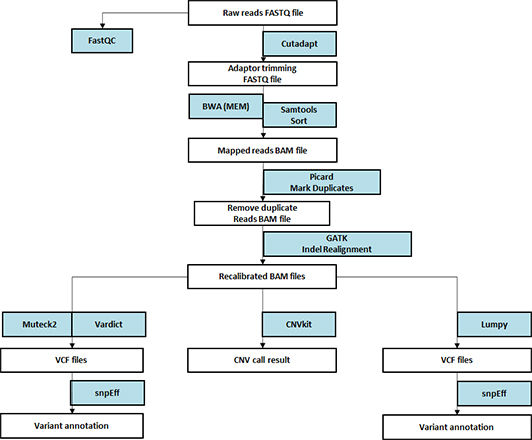
-
Standard Analysis
Read mapping
Variant calling
Variant annotation
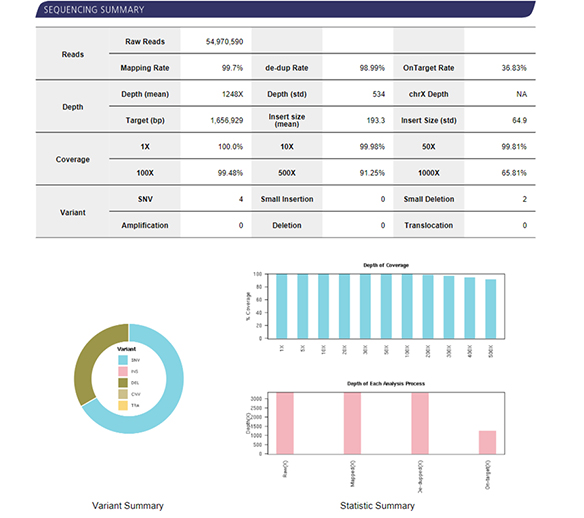
-
Advanced Analysis
Genomic rearrangement
Tumor mutation burden (TMB), Microsatellite instability (MSI)

Features & Benefits
- 임상 검사의 목적의 Targeted Sequencing Panel에 대한 변이체 탐색
- 국가 암 정보과제로 증명된 변이체 탐색
- 변이체 발굴을 통하여 임상의들의 환자 질병 치료에 대한 의사결정 과정에 가이드 제공
Reference
[1] Kim, H. S. et al., (2018). Association of PD-L1 Expression with Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Mutation Burden in High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 13(5), 636–648.




